DUCTF23 - Eight Five Four Five
Eight Five Four Five
Disclaimer: This is the first blockchain challenge I have done, so the technical aspects about smart contracts for this writeup can be inaccurate.
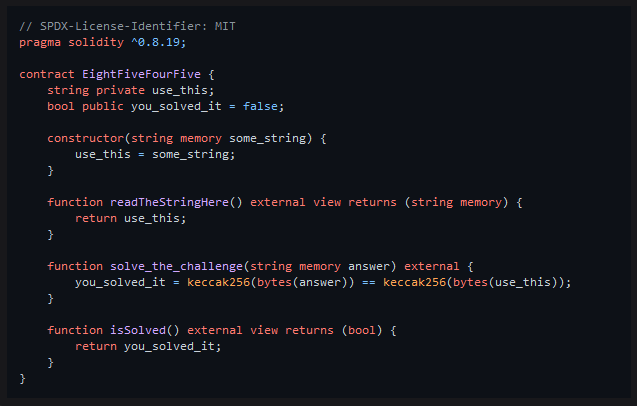
The contract for this challenge is written in Solidity
This is a beginner blockchain challenge that is supposed to just learn players how to interact with smart contracts. For this I used the python-library Web3.
Before we are able to interact with the smartcontract we need to get the ABI of the smart contract, which is the standard way to interact with contracts in the Ethereum ecosystem. Once we have the ABI of the contract we are able to call functions defined in the given contract. compile.py compiles the challenge-provided smart contract EightFiveFourFive.sol with solcx to give us the ABI for the contract.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import solcx
#solcx.install_solc("0.8.19")
temp_file = solcx.compile_files(
'EightFiveFourFive.sol',
output_values=['abi'],
solc_version='0.8.19'
)
abi = temp_file['EightFiveFourFive.sol:EightFiveFourFive']['abi']
Looking at the smart contract we are given we can see three functions that we are able to call
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
function readTheStringHere() external view returns (string memory) {
return use_this;
}
function solve_the_challenge(string memory answer) external {
you_solved_it = keccak256(bytes(answer)) == keccak256(bytes(use_this));
}
function isSolved() external view returns (bool) {
return you_solved_it;
}
The contract also use two variables, where one is private and one is public.
1
2
string private use_this;
bool public you_solved_it = false;
To solve the challenge we need to change the you_solved_it variable to true, which can be done by reading the private variable use_this through calling the readTheStringHere function, and calling the function solve_the_challenge with the value of use_this as an argument. The solve_the_challenge changes you_solved_it to True if the two keccak256 hashes match, e.g. our argument passed to the function must match with the private variable.
Our smart contract instance gives us the RPC-url, Contract address, Private key, and Wallet address needed to create a connection to the contract.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
rpc_url = "<rpc_url>"
contract_address = '<contract_addr>'
private_key = "<pk>"
wallet_address = "<wallet_addr>"
# Create web3 connection
web3 = Web3(Web3.HTTPProvider(rpc_url))
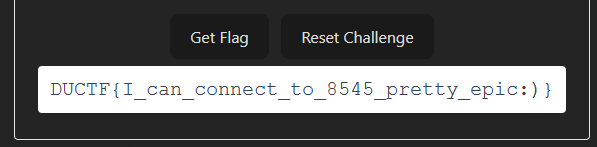
We also need to create an instance of the contract, which we will use to call its functions. With this we can obtain the secret value we need to get the flag (the secret value is I can connect to the blockchain!).
1
2
3
# Create contract instance and get the secret by calling readTheStringHere()
contract = web3.eth.contract(address=contract_address, abi=abi)
secret = contract.functions.readTheStringHere().call()
Once we have the secret value we can call the solve_the_challenge function, however this is not as easy to do as when we called readTheStringHere.
To call the solve_the_challenge function with the secret as the argument we need to build and create a transaction. For that we need a nonce, which can be obtained with the web3 function get_transaction_count (the nonce is a value which indicates the transaction count from a wallet address). We also need a gasPrice, which in short terms is the price for executing a function. We can just set this to 1 and let web3 handle the rest. We also set the chainId parameter to the value given to us from the launched challenge instance.
1
2
3
4
5
6
nonce = web3.eth.get_transaction_count(wallet_address)
tx = {
"nonce": nonce,
'gasPrice': web3.to_wei('1', 'gwei'),
'chainId': 31337
}
Finally we can create the transaction for calling solve_the_challenge(secret) by building the transaction, sign it using our given private key, and sending the transaction to the smart contract server.
1
2
3
4
# Create, sign and send transaction
txn_data = contract.functions.solve_the_challenge(secret).build_transaction(tx)
signed_txn = web3.eth.account.sign_transaction(txn_data, private_key=private_key)
web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_txn.rawTransaction)
The full script is provided below
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
import requests
from compile import abi
from web3 import Web3
rpc_url = "<rpc_url>"
contract_address = '<contract_addr>'
private_key = "<pk>"
wallet_address = "<wallet_addr>"
# Create web3 connection
web3 = Web3(Web3.HTTPProvider(rpc_url))
# Create contract instance and get the secret by calling readTheStringHere()
contract = web3.eth.contract(address=contract_address, abi=abi)
secret = contract.functions.readTheStringHere().call()
# Setup required fields for transaction
nonce = web3.eth.get_transaction_count(wallet_address)
tx = {
"nonce": nonce,
'gasPrice': web3.to_wei('1', 'gwei'),
'chainId': 31337
}
# Create, sign and send transaction
txn_data = contract.functions.solve_the_challenge(secret).build_transaction(tx)
signed_txn = web3.eth.account.sign_transaction(txn_data, private_key=private_key)
web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_txn.rawTransaction)
Running the script allows us to get the flag through the frontend we are given for the contract.